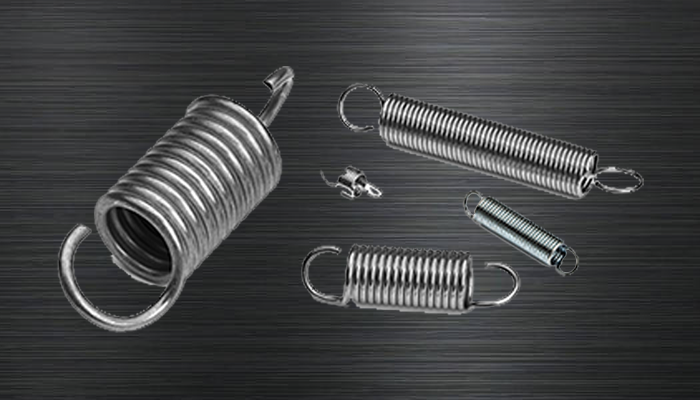
Extension springs
Extension springs absorb and store energy as well as make a protection from a pulling force. These springs are regularly connected at the both finishes to different parts and when these parts move separated, the spring attempts to unite them back once more.
Product Description
Uses of Extension Springs:
- Very much useful in car interiors and exteriors
- Also used in carburettors, toys, farm machinery and etc
- Long Helping Life.
- These are also used in garage doors
- Largely Self-damping, giving great shock assimilation and energy dissemination.
- Washing devices also need extension springs
Formulas on extension springs:
| To calculate wire diameter, |
| (OD - ID) ÷ 2 = WD |
| To calculate the outer diameter, |
| 2WD + ID = OD |
| To calculate inner diameter, |
| OD – 2WD = ID |
| To calculate mean diameter, |
| OD – WD = MD |
| ID + WD = MD |
| To calculate load |
| R = Load(L) / Distance travelled(Dt) |
Types of Expression Springs:

1. Machine Hooks:
Machine hooks are typically attached to the ends of extension springs to provide a means of securely attaching the spring to other components or anchor points. The hooks may be formed in a variety of shapes, including straight, curved, or angled, depending on the specific application requirements.

2. Center Hooks:
Center hooks are typically attached to the center of the extension spring to provide a means of securely attaching the spring to other components or anchor points. The hooks may be formed in a variety of shapes, including straight, curved, or angled, depending on the specific application requirements.
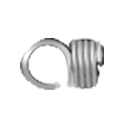
3. Side Hooks:
Side hooks are typically attached to the ends of the extension spring, with the hook positioned perpendicular to the spring axis. This allows for the spring to be attached to other components or anchor points from the side, rather than from the end. The hooks may be formed in a variety of shapes, including straight, curved, or angled, depending on the specific application requirements.

4. No Hooks :
No hooks is a type of extension spring configuration where the ends of the spring are not formed into hooks, loops, or other attachment mechanisms. Instead, the ends of the spring are left straight, allowing the spring to be attached to other components or anchor points using other means, such as threaded bolts or clips.
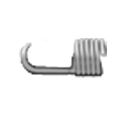
5. Extended Hooks:
Extended hooks are typically attached to the ends of the extension spring and are formed to extend beyond the end of the spring. This allows for the hook to be easily attached to other components or anchor points. The hooks may be formed in a variety of shapes, including straight, curved, or angled, depending on the specific application requirements.



